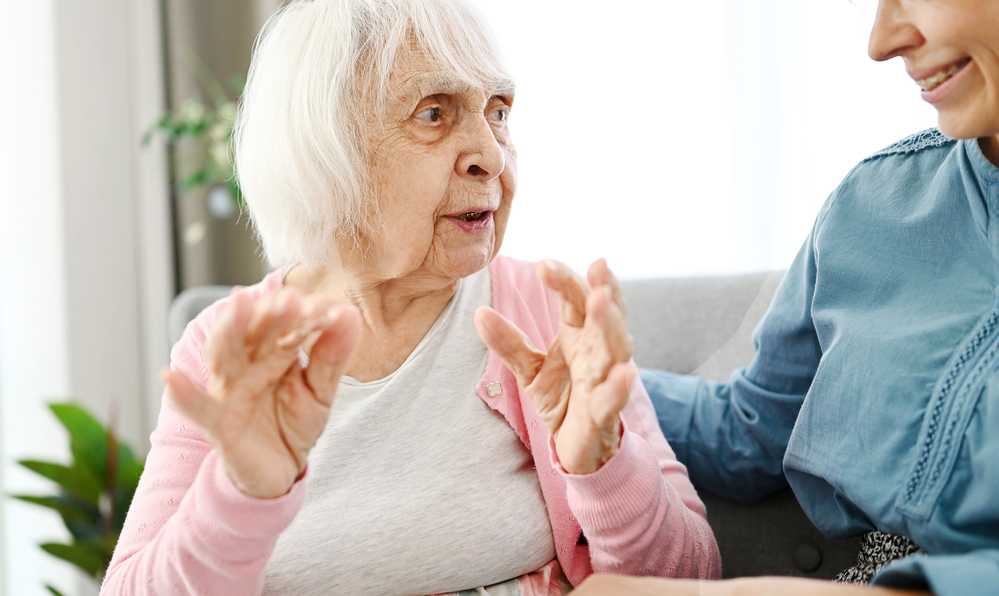
In the realm of mental health and wellness, Reminiscence Therapy[1] has emerged as a profound tool for fostering emotional and cognitive well-being, particularly among older adults and those with cognitive impairments. But what is it about reminiscing that makes it so beneficial? Let’s delve into the science behind Reminiscence Therapy to understand how this practice can heal and transform lives.
Understanding Reminiscence Therapy
Reminiscence Therapy[2] involves the guided recall and discussion of personal memories, often facilitated by a trained therapist or caregiver. This process can include storytelling, sharing photographs, listening to music, or engaging with other memorabilia that evoke memories. The goal is not merely to remember but to reflect and interpret these memories in a way that promotes mental and emotional health.
Cognitive Benefits: Strengthening Neural Pathways
One of the key scientific principles behind Reminiscence Therapy is its impact on the brain’s neural pathways. Our memories are stored in complex networks of neurons. When we recall a memory, these neurons are activated, strengthening the connections between them. This process is especially important for older adults and individuals with dementia or Alzheimer’s disease.[3]
Studies have shown that engaging in Reminiscence Therapy can slow cognitive decline by stimulating areas of the brain associated with memory and cognition.[4] For example, research published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease found that Reminiscence Therapy significantly improved cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer’s compared to traditional care methods. This suggests that regularly revisiting past experiences can help maintain cognitive abilities and potentially slow the progression of degenerative diseases.
Emotional Benefits: Enhancing Mood and Self-Esteem
The emotional benefits of Reminiscence Therapy are equally compelling. Reflecting on positive past experiences can evoke feelings of joy, satisfaction, and pride. This emotional uplift can reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, common issues among older adults.[5]
Psychological theories suggest that Reminiscence Therapy helps individuals process and make sense of their life experiences, leading to a more integrated and positive sense of self. A study in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry found that Reminiscence Therapy reduced depressive symptoms in older adults by helping them focus on positive life events and achievements, thus boosting their self-esteem and overall mood.
Social Benefits: Building Connections
Social interaction is another critical component of Reminiscence Therapy. Sharing memories in a group setting or with family members can foster social bonds and reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation. Human beings are inherently social creatures, and sharing personal stories can create a sense of community and belonging.[6]
A study published in the Aging & Mental Health journal found that group Reminiscence Therapy significantly improved social interaction and communication skills among participants. This is particularly beneficial for individuals in nursing homes or assisted living facilities, where social opportunities might be limited.
Therapeutic Benefits: Processing Trauma and Loss
For individuals dealing with trauma, loss, or unresolved emotions, Reminiscence Therapy offers a safe and structured way to process these experiences. Revisiting and discussing difficult memories can help individuals gain new perspectives and come to terms with past events, facilitating emotional healing.
Neuropsychological research indicates that talking about traumatic experiences in a supportive environment can reduce the intensity of negative emotions associated with those memories.[7] This therapeutic process, known as reconsolidation, helps individuals reframe their past in a way that diminishes its emotional impact.
The Future of Reminiscence Therapy: Technological Advancements
As our understanding of Reminiscence Therapy grows, so too does the potential for innovative applications. Digital tools[8] and virtual reality (VR)[9] are being explored as new ways to enhance the therapy experience. For instance, VR can immerse individuals in recreated environments from their past, providing a vivid and engaging way to stimulate memories.
Preliminary studies on the use of VR in Reminiscence Therapy have shown promising results, suggesting that technology can enhance the effectiveness of traditional methods by providing more immersive and interactive experiences.
Conclusion
The science behind Reminiscence Therapy underscores its powerful impact on mental and emotional health. By engaging with and reflecting on our past, we can strengthen cognitive functions, boost emotional well-being, foster social connections, and process difficult experiences. As research continues to evolve, Reminiscence Therapy stands poised to become an even more integral part of holistic care, demonstrating the profound healing power of our memories.
[1] Latha, K. S., et al. “Reminiscence Therapy: An overview.” Middle East Journal of Age and Ageing 11.1 (2014): 18-22.
[2] Park, Kyongok, et al. “A systematic review and meta-analysis on the effect of reminiscence therapy for people with dementia.” International psychogeriatrics 31.11 (2019): 1581-1597.
[3] Duru Aşiret, Güler, and Sevgisun Kapucu. “The effect of reminiscence therapy on cognition, depression, and activities of daily living for patients with Alzheimer disease.” Journal of geriatric psychiatry and neurology 29.1 (2016): 31-37.
[4] Cuevas, Pearl Ed G., et al. “Reminiscence therapy for older adults with Alzheimer’s disease: a literature review.” International journal of mental health nursing 29.3 (2020): 364-371.
[5] Chiang, Kai‐Jo, et al. “The effects of reminiscence therapy on psychological well‐being, depression, and loneliness among the institutionalized aged.” International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry: A journal of the psychiatry of late life and allied sciences 25.4 (2010): 380-388.
[6] Laidlaw, Robert John, et al. “Improved Mental Health, Social Connections and Sense of Self: A Mixed Methods Systematic Review Exploring the Impact and Experience of Community Reminiscence Programs.” Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare (2023): 4111-4132.
[7] Wu, Li‐Fen. “Group integrative reminiscence therapy on self‐esteem, life satisfaction and depressive symptoms in institutionalised older veterans.” Journal of Clinical Nursing 20.15‐16 (2011): 2195-2203.
[8] Lazar, Amanda, Hilaire Thompson, and George Demiris. “A systematic review of the use of technology for reminiscence therapy.” Health education & behavior 41.1_suppl (2014): 51S-61S.
[9] Tominari, Maho, et al. “Reminiscence therapy using virtual reality technology affects cognitive function and subjective well-being in older adults with dementia.” Cogent Psychology 8.1 (2021): 1968991.